Let us know our Forests and Wildlife – Monthly talk by Mr. Bharat Pathak
(Summarized by a SciParent – Mrs. Rajvi Mehta)

Introduction:
In celebration of Wildlife Week, SciKnowTech, in association with Finar Foundation, experienced another successful and its 3nd session of “Monthly FunXploring Talks” on 7th Oct 2018. “Let us Know Our Forest & Wildlife” – A highly engaging and informative talk by Shri Bharat Pathak.

Shri Bharat Pathak is a retired Indian forest service officer. At the time of retirement he was holding position of Additional Principal Chief Conservator of Forests in Gujarat Forest Department with more than 40 years experience on total Forestry and Wildlife Services. Post retirement he has been into VIKSAT, Voluntary Organization for Sustainable Development as Director and Director in State Institute of Rural Development Gujarat. He is actively involved in various activities like:
- Member, Central Zoo Authority and its Technical Committee, Government of India,
- Member, Gujarat Biodiversity Board, Government of Gujarat.
- Honorary State Academic Coordinator for the National Children Science Congress since last three years for the state of Gujarat.
- He has authored few books which are being used as the main reference book in conservation of flora and fauna in the state.
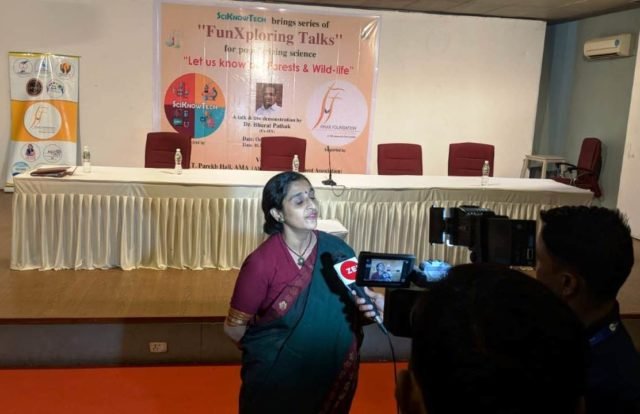
The talk was covered by Z-News.


WHAT IS ECOLOGY OR ECOSYSTEM OF GUJARAT?
The talk was kickstarted in conjunction with experiential learning suggestions from Shri Bharatbhai Pathak. He mentioned Nal Sarovar, Thol Bird Sanctuary and Indroda Nature Park are the closest places from Ahmedabad to study Ecology or Ecosystem of Gujarat.
Existence of wildlife directly depends on presence of Forest and Water body. Forest and Water provide environment and food for the wildlife. Gujarat hosts 4 main types of Forest ecosystem out of 16 major forest types available in India. Read more about Forest types here. Of total geographical area of the Gujarat State, ~11% area is occupied by Forests. National avg is ~24%. Gujarat has longest coastline of 1600 Kilometers (24% of Indian Coastline) which organically hosts plenty of aquatic wildlife. Hence, the fact that even if Gujrat is Forest Poor State, it has Rich Wildlife.
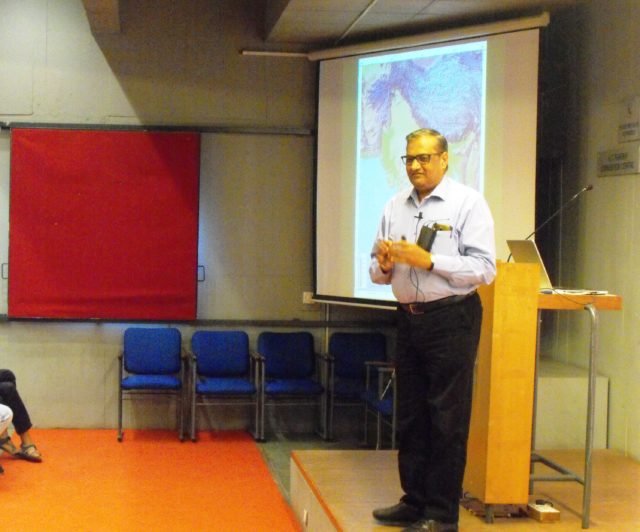
As this interactive talk progressed, it made sense to audience that, in Gujarat, existence of forest highly depends on presence of Mountains. This is due to urbanization and increased use of land for agricultural purpose. Shri Pathak then showed kids & parents various maps which include different mountain ranges associated with Gujarat, Rivers, Gulf, Kutch desert etc. With each he explained how it contributes habitating wildlife and what kind of wildlife different places host.

‘ECOLOGY’ & ‘ECONOMY’:
Oikos and Logia are originally greek word meaning home and study. Hence the word Ecology means study of home. Word Nomia means manage. Hence, both these words come from same roots. As it also makes practical sense, they should be considered in parallel to each other and not as opposite. In current time people consider these as opposite as preserving ecology seems to have no benefit related to money or economy. Example: Cut trees to build cities and housing.
Further explaining the context in which the term ‘manage’ should be used, Mr. Pathak explained how one’s home is a system where there are set of rules to be followed. If such rules are not followed, it affects the ecosystem resulting negative impact on the equilibrium of the system.

HOW HUMAN INTERVENTION INTO FOREST ECOSYSTEM HAS AFFECTED FOREST AND WILDLIFE?
Over the years, deforestation is taking place on the earth. Specific to land structure like Gujarat where most land is flat, the motive to deforest is to promote agriculture. Hence it now makes sense why Mountain Ranges associated with Gujarat are important for presence of Forest and Wildlife.
Roughly 10000 years back cultivation activities started. Before then humans were hunters and food gatherers. Hence with advent of civilization human activities started impacting the ecosystem. Earlier human was living as part of ecosystem. Hence, planting new trees to reforest is important.
WHAT IS WILDLIFE:
Any and all animals, reptiles, birds, all aquatic animals etc that live in wild and not domesticated or controlled by human is part of wildlife.
WILDLIFE IN GUJARAT:
- Earlier there used to be tigers in South East part of Gujarat.
- Kutch Little Rann: 300 types of birds as well as Jhinga(fish).
- Narayan Sarovar: Thorn forest hosts Chinkara
- South of it is wetland Chhari for Eagle/Hawks & other birds
- Nalsarovar Sarovar sanctuary.
- Blackbuck National Park
- Gir National Park
- Girnar Wildlife Sanctuary
WHAT IS FOREST:
Forest in its most simplest term could be defined as an area where Trees are of predominance. It also consists all forms of plants and hosts some wildlife too.
FORESTS IN GUJARAT:
Of 16 types of forests available in India, Gujarat hosts 4 types.
- Tropical Moist Deciduous Forests
- Tropical Dry Deciduous Forests
- Northern Tropical Thorn Forests
- Littoral and Swamp Forests
Benefits of forests with reference to the rain water:
Forest retains large amount of water in the soil preventing it from immediately draining into ocean. Hence, prevents flooding. This stored water is slowly getting released which is eventually used by wildlife, agriculture and is in a way an excellent ecoservice.
MOUNTAIN RANGES ASSOCIATED WITH GUJARAT:
- Sahyadri (Western Ghat): Starts in Songadh town of Gujrat and runs from north to south. It passes through Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- Satpura: Starts in east part of Gujarat and runs through Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh to the east in Chhattisgarh.
- Arvalli: starts in North India from Delhi going southwest ending in Gujarat. It is also known for it being the oldest mountain system. Himalayas are gigantic but newer.
- Vindhya: In past, based on some resources and how one defines it.
- Girnar Mountain Range in Junagadh District: holds peak of Gujarat land at 1113 meters.
DESERTS IN WEST:
- Little Rann of Kutch
- Great Rann of Kutch
Are salt marsh, which is desert under the water. It is wetland after monsoon and produce salt when dry.
GULFS:
Out of 3 Gulfs in India, Gujarat hosts 2.
- Gulf of Kutch
- Gulf of Khambhat
RIVER AND RIVER VALLEYS:
- Tapi which flows through Melghat Tiger Reserve
- Nal Sarovar – A natural lake
RAINFALL IN GUJARAT:
- South East of Gujarat enjoys high rainfall with avg 60 rain days a year making the area moist.
- North West of Gujarat experiences low rainfall with average 15 rain days a year making the area aried.
Q&A:


Along with few questions here and there during the talk, it became more interesting and interactive when Mr. Pathak guided Q&A session at the end of the talk.
Mr Pathak: How many different types of birds can be observed in Gujarat?
Yatharth Jain (Grade 8, SGVP): Around 500 different types!!!
Mr. Pathak: What can you possibly see at Pirotan Island?
Maanit (Grade 8, Anand Niketan): Dolphins, Mangroves, Coral Reef
Question from audience: Why Coral, Mangroves are important?
Maanit Patel (Grade 7, Riverside): They support fishes and provide them food.
Question from parent in audience: Why to preserve Wildlife?
Ansh Shah (Grade 4, Prakash school) provided the spot on and crisp answer.
To maintain the equilibrium of interdependence between plants and animals.
Fun Facts:
- From Gujarat’s coast one can catch 80 different types of fishes and hence Gujarat coast provides highest amount of fishing in entire India.
- Wolf can be spotted in Little Rann of Kutch, Velavadar, Bhal and Dahod.
- Gujarat has 2nd highest presence of Mangrove Forest which groves on clay soil with intertidal area.
The discussion ended with brief introduction about Silviculture based on question that Krisha asked.


Further Reading: https://forests.gujarat.gov.in/forest-area.htm


